
Microcontrollers
October 19, 2021 David Lancaster 0Our world is filled with electronic products that entertain us, make our lives easier, allow us to communicate with each other, help us prevent diseases, and much more.
More often than not, at the heart of all these electronic products is a Microcontroller.
This awesome device is the brain that controls all actions and takes care of computations within an electronic device.
Because of its endless capabilities, there are many uses of microcontroller and it is not confined to one singular application
A microcontroller can be found in applications such as consumer electronics, medical devices, the automotive industry, aviation, marine, and much much more.
This article shall take an in-depth look at the microcontroller and its many applications.
To better understand why a microcontroller is used for a specific application, it will help to take a closer look at its history, how it is constructed, the different types available, etc.
The world is filled with electronic devices that have a specific purpose whether it be playing music, making coffee, toasting bread, etc.
I would be surprised if you didn’t find a Microcontroller at the center of most of these systems.
A microcontroller is an Integrated Circuit (IC), which has all the capabilities of a computer. It consists of a central processing unit (CPU), onboard memory and inputs/outputs all of which are programmable.
A microcontroller has the task of ‘controlling’ operations (much like a traffic cop controls traffic) hence why the second half of its name is ‘controller’. The ‘micro’ is aptly there because of its size.
It is used by professional engineers, students, and hobbyists for many different applications (which shall be discussed in more detail later).
The field of electronics has been around for some time. But, the microcontroller wasn’t the star of the show from the very beginning.
It came to the forefront of electronics a bit later.
Before the arrival of the microcontroller, Logic Gates were used to perform Boolean logic functions (which is the basis of digital electronics).
These logic gates were built using Transistors. A large assembly of logic gates would form many digital circuits (which meant many transistors).
Later, with the invention of Integrated Circuits, many transistors could be fitted onto a single chip (this meant a reduction in size of digital circuits).
By the early 1970’s these integrated circuit chips could hold as many as 10,000 transistors. This crucial advancement in digital electronics is what made the invention of the microcontroller possible.
We can thank one Gary Boone, who worked for Texas Instruments for giving the world the first ever microcontroller in the early 1970s.
He designed and created an integrated chip that had over 5000 transistors, 3000 bits of program memory, and 128 bits of access memory.
This meant it but could be programmed to have a variety of functions.
This first microcontroller was called the TMS1802NC.
Over the years, the microcontroller has had further advancement with the help from many different companies.
In the early 1990’s Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM), meant that the microcontroller wasn’t limited to one function for its lifetime after it had been programmed.
Now, you could program the microcontroller, erase the current program, and reprogram it multiple times.
At the start I briefly mentioned some of the applications of the microcontroller. But, those are just a few of the many applications.
Rather than name every single device that uses a microcontroller, I will name the main fields under which devices are most likely to use them.
Note, this isn’t an exhaustive list by any means. These are just the most common.
Let’s take a look!
First on the list is Consumer Electronics.
Consumer electronics is a term that defines electronic equipment that is used on a daily basis (mostly in one’s own home).
This is a very broad term that encompasses many other categories such as Entertainment, Communication, Recreation, Kitchen Appliances, etc.
Consumer electronics are often referred to as ‘black goods’ due to their electronics being housed in a dark casing.

The Medical field has benefited immensely from using microcontrollers.
As you can imagine, medical practices before the advent of the microcontroller would have been quite primitive.
Also, we have all heard the phrase ‘prevention is better than cure’. In the medical applications this means that if you can find a problem at the early stages, you have more chances of eliminating it.
While us humans have amazing abilities, and intelligence, there is a limit to what we can detect within a human body.
Microcontrollers, along with other technology enable us to be able to detect a disease with a human body before it is too late.
Microcontrollers can also now be found in the surgery room. Robots are used to help surgeons with many different types of surgeries.
In the age before electronics and microcontrollers you might have been limited to a few activities to help pass your time. Things like reading a book, going for a walk, playing the guitar, playing hide and seek, etc (Not that any of these are bad).
Nowadays, we are all spoiled with a plethora of devices to entertain ourselves.
Even before the microcontroller, there were electronic devices which could help entertain and pass your time.
But, these devices grew not only in quantity, but complexity and quality as well with the help of the microcontroller.
Your old transistor radio might have been limited to a couple of stations, with subpar sound quality. But, now your digital radio will have the capability to access all stations on the FM and AM bandwidth with superior sound quality, while being able to play CDs as well.

Instrumentation and Process control is a field of Engineering that deals with control theory. It is used to manufacture equipment to help design, monitor, and control many different processes across many different industries.
These processes ensure that the overall system is productive, efficient, and repeatable.
The overall system consists of software and hardware which includes, sensors, actuators (mechanical and electrical), and of course a microcontroller.
For example, in a chemical plant,having a system that monitors the temperature and ensures it stays within defined limits is crucial to avoiding potential disasters such as explosions.
Communication is a necessity in everyday life. They say communication is one of the pillars to a happy marriage (so it must be very important!).
We use communication for many different purposes; to share information, make a statement, ask questions, express wants/needs/desires, keep in touch with loved ones, express emotions and much more.
But, most of the time you might not be in the same room with the person you might want to communicate with.
They might be in another household, city, or country.
Before you might have had to write them a letter, post it and wait a couple weeks for a reply.
Lucky for you and me, nowadays, microcontrollers are used in many of these electronic communication devices to allow us to communicate with loved ones, colleagues, strangers, instantaneously, even if they are in another country (they might as well be in the same room as us!).

Whether you are an Accountant, Engineer, IT specialist, Receptionist, work in Human Resource, etc, you will more often than not be working in an office environment.
This is the space where you carry out your daily tasks which help take the company you work for closer to their goal whatever it may be.
These tasks might be specific to your job, or might be similar across different disciplines.
There are a myriad of electronic equipment which have microcontrollers to help you complete tasks in a more efficient manner (helping keep your boss happy).
Imagine having to wake up, go outside, collect firewood, start a fire, and then prepare your breakfast. These are a lot of steps to just make an omelette.
Also, imagine having to repeat the process for lunch and dinner. This would get annoying quite fast.
Luckily, people realised this early on and created devices that are much more efficient at preparing and making food and drinks in the kitchen.
These days our kitchens are filled with appliances that make many cooking tasks much more efficient as well as tasks that we might not be able to accomplish, like preserving food.

There are many mundane tasks that we need to carry out around the house.
Tasks like washing the clothes, drying the clothes, washing the dishes, cleaning the floor, cleaning the toilet, and the list goes on.
Without sounding like a broken record, we are blessed these days with electronic devices that help make these mundane tasks, well, less mundane!
Unfortunately, the world is filled with many dangers.
But, we cannot live our lives scared all the time of every danger that exists. This is not what living should be.
However, having systems in place to ensure that we are aware of dangers, or when a danger is imminent, is the best way to avoid injury or death.

Whether you need to go to your local grocery store, across the ocean to another country, and now even space, you can do so thanks to the advancement in Transportation
Microcontrollers are used extensively within sub-systems of cars, motorbikes, boats, ships, trains, aeroplanes, spaceships, for a variety of different functions (safety, guidance, monitoring, etc).
But, what is the main purpose of using a microcontroller for these applications?
As I mentioned earlier, the microcontroller has the main task of making computations and controlling tasks much like a traffic cop directing traffic.
A better analogy and way to visualise this is the human body.
So, the human body will represent an electronic system. It has many inputs (senses), outputs (muscles), and other subsystems (organs such as the heart, liver, kidney, etc).
The brain is one of the most important pieces of the human body (the other being the heart of course). The brain best represents the functionality of the microcontroller.
It receives signals from your senses, and sends signals to other parts of the body like the organs and muscles, controlling the overall operation.
An embedded system is the combination of hardware and software components.
Microcontrollers are used in the exact same manner in embedded systems in many of the applications we just covered.
They ensure that all parts of the system work cohesively to achieve what that specific system was created to do.
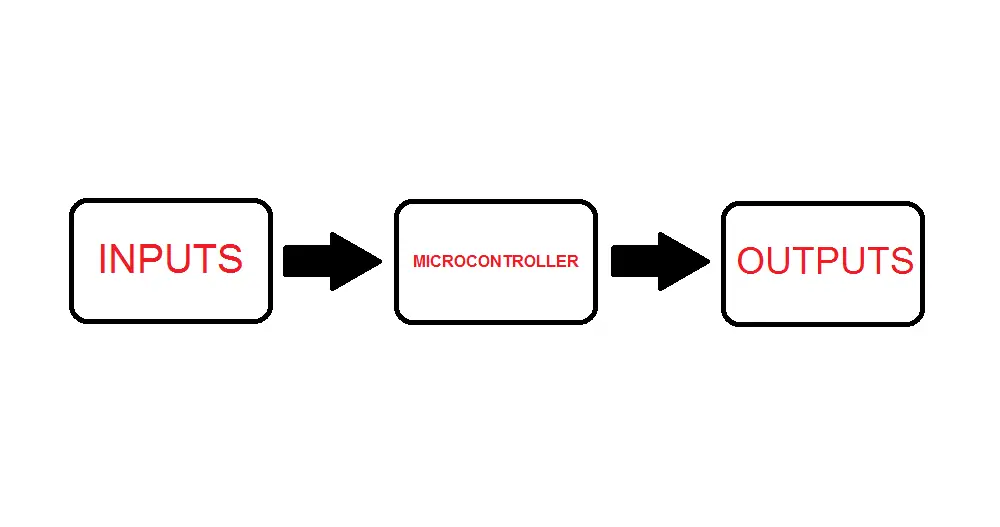
The flowchart above shows the typical flow of information within an embedded system.
Even though the first microcontroller was created by Texas Instruments, there have been many other companies who were part of the initial race to create the first microcontroller, as well as others who joined later on.
While the overall purpose of each microcontroller stays the same, the Architectures on which they are built on will vary across different manufacturers.
There are two main architectures which microcontrollers are built on; Harvard and Von-Neumann.
Harvard Architecture defines separate memory spaces for program and data which allows both to be accessed at the same time.
Whereas in the Von-Neuman architecture, data and programs are stored in the same memory space.
Also, there are many other microcontroller features such as number of inputs, outputs, Timers, etc, (which will be discussed in more detail in the next section) which will vary from one manufacturer to the next.
Below are the different manufacturers of microcontrollers;
First on the list has to be Texas Instruments. Their microcontrollers range in 16-bit and 32-bit options, which are high-performance and low in power consumption. They are also available in wired and wireless options. There are a range of software and development tools to help you implement your ideas faster.
Cypress semiconductor offers low-power and high performance microcontrollers tailored towards consumer, industrial, and automotive applications.
Infineon is one of the leading companies in the microcontroller scene based in Germany. They create 32-bit microcontrollers which are ideal for connectivity, safety and security.
Maxim Integrated develops robust 32-bit microcontrollers for Internet Of Things (IOT) applications. Their microcontrollers offer the biggest memories with efficient power management They also integrate high cryptography for high levels of security.
Microchip are at the forefront of the development of microcontrollers which offer a range of options which include 8-Bit, 16-Bit, and 32-Bit. They provide many software libraries and design options making them a first choice for many customers.
NXP also offers 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit microcontrollers, which combine the technologies of Kinetis and LPC.
Have a range of 8-bit and 16-bit microcontrollers for general and specific applications. Applications like Radio Frequency applications because of their ultra-low power consumptions.
A well known name for many electronic devices, Panasonic also manufactures microcontrollers. They are used for many different applications as they combine high performance and low power consumption.
Another dominating name in the industry, STMicroelectronics provides a large portfolio of microcontrollers which are very robust. Features include power, efficiency, security, high performance and scalability.
Microcontrollers come in a variety of shapes, sizes, as well as features.
These features are crucial in choosing the right microcontroller for the right applications.Let’s take a brief look at the different features.
We now know that a microcontroller consists of a CPU, memory, and other various peripherals all contained within a single chip.
The first major feature when looking at a microcontroller is its CPU Size, which refers to the bit-width.
In the early days, you were limited to 4-Bit microcontrollers which meant they had a 4-Bit CPU. But, what does having a 4-Bit CPU mean?
This meant that operations were carried out using 4-bit numbers, variables were stored in 4-bit blocks, and inputs/outputs were accessed via 4-bit data busses.
Nowadays microcontroller CPU sizes are available in 8-Bit, 16-Bit, 32-Bit and 64-Bit.
If we break down the microcontroller into modules, you would see that it is composed of digital circuits. There are two types of digital circuits; Combinational and Sequential.
The digital circuits inside a microcontroller are Sequential.
In order to function properly, these sequential circuits require a Clock.
The main job of the clock is to manage the operations between different blocks within the microcontroller such as the CPU, memory, and peripherals (just like a microcontroller has the job of managing the operations of an embedded system).
The Clock Frequency is the speed at which the microcontroller is able to manage these operations.
Instructions are executed at every ‘tick’ of the microcontroller clock. So, the higher the clock frequency, the faster that instructions can be executed.
So a microcontroller with a clock frequency of 1MHz is able to complete 1 million instructions per second.
Common clock frequencies of microcontrollers 1MHz, 8MHz, 16MHz, and 32MHz.
Another major building block, Memory is a crucial part to every microcontroller. Memory is used to store data such as program code, and variables.
There are two two types of data; data that does not change and data that changes during program runtime.
A microcontroller will typically have three different types of memory; SRAM, FLASH and EEPROM to accommodate these two types of data.
SRAM (static random-access memory) – This type of memory holds data that can be accessed and changed during runtime. SRAM is volatile memory which means that when power is removed, all data stored in SRAM is lost.
FLASH – Holds memory that does not change and is where the program memory is stored.
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory) – EEPROM is similar to SRAM, in that it can be accessed and changed during runtime. However, this type of memory is non-volatile, which means that the data remains even after power is removed.
An input device sends information to a microcontroller, whereas information is sent to an output device to control it.
There are a multitude of input and output devices that can be interfaced to a microcontroller;
Inputs such as buttons, switches, sensors, variable resistors, and outputs such as motors, Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), Liquid Screen Displays (LCDs), etc.
The microcontroller has General Purpose Input Output (GPIO) ports that these I/O devices are connected to.
GPIO ports of a microcontroller are Bi-Directional which means that they can be programmed to be either an input or output.
Note, these ports are limited to the amount of current they can sink (as an input) and source (as an output). You will need to consult the microcontroller’s datasheet to check these values.
Timing is crucial in all aspects of life.
It governs how long our workdays are, how long we exercise for, flight departures and arrivals, when to eat food, and so much more.
Timing is also crucial when it comes to microcontrollers.
Timers are modules within a microcontroller which are used for setting precise delays, calculating time between events (internal and external), and generating PWM.
They are linked to the system clock we saw earlier. However, with the help of something known as a prescaler, the main clock speed can be scaled down to generate slower speeds.
Most microcontrollers come with a 16-Bit and an 8-Bit timer.
16-Bit timers count up to a digital value of 65535, and 8-Bit timers count up to 255.
16-Bit timers have a greater resolution which gives you more options for the number of delays you can generate.
One of the many input devices that are used with microcontrollers are Sensors.
Sensors have the ability to detect changes in the real world and provide an analog voltage at its output (which is sent to the microcontroller).
For example, a temperature sensor detects changes in the ambient temperature and outputs an analog voltage accordingly.
However, microcontrollers are devices that only deal with digital data. For that reason, it has a module known as an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC).
As the name might suggest, it takes an analog voltage and converts it to a digital value which the microcontroller can use for further processing.
On the other side, you might want to take a digital value and convert it to a digital value. This can be done with the help of a Digital to Analog Converter (DAC).
PWM outputs 000
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is the process of being able to generate different levels of an output signal.
This is achieved by varying the ratio (which is known as the Duty Cycle) of time that a signal is ‘on’ vs the time that it is ‘off’. PWM signals are square waves.
PWM has many applications, with the main ones being; motor speed control, and brightness control of Light Emitting Diodes.
As we saw earlier, the Timers have capability to generate PWM. A microcontroller also has designated PWM output pins where you connect outputs such as motors, and Light Emitting Diodes.
While the microcontroller is a stand alone device, sooner or later it is going to need to communicate with peripheral devices (Liquid Crystal Displays, Bluetooth modules, accelerometers, etc), as well as other microcontrollers.
There are two ways of communication; Parallel and Serial.
Parallel communication involves transferring 8-Bits of data at the same time, across eight individual data lines to parallel input/output devices.
Serial communication transfers one bit of data at a time. While this is slower, it solves many of the problems associated with parallel communication mentioned above.
A microcontroller is limited by the number of pins it has, so serial communication is ideal when it comes to designing a system.
There are two main types of serial communication; Asynchronous and Synchronous.
Asynchronous serial communication is not synced with the main clock (data transfer happens at random time intervals). The Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART) is the most common method that a microcontroller uses for asynchronous serial communication.
Synchronous serial communication is synched with the main clock (data transfer happens at known time intervals). Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) and Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) are two common protocols that a microcontroller utilises for synchronous serial communication.
Interrupts are certain conditions that cause the microcontroller to temporarily jump out of the normal program and execute the code within the interrupt.
Interrupts can be caused by Internal or External circumstances.
Internal interrupts are when a certain condition is met within the microcontroller modules. For example, if you are using an 8-Bit timer to count to a certain value, there is a certain interrupt called Compare Match specific for the 8-Bit timer that is executed when the timer value ‘matches’ the value you set.
External interrupts are when certain physical events occur outside of the microcontroller at one of its pins (a microcontroller will usually have a couple pins dedicated for external interrupts). These events could be things like a ‘button press’.
Last on the list of notable features of a microcontroller are Sleep Modes.
You might be wondering, why the heck does a microcontroller have sleep modes? It’s a machine, it should be able to work overtime all of the time!
However, sleep modes are an essential to microcontrollers.
The main purpose of them is to conserve energy.
If you are designing a portable embedded system that runs off disposable or rechargeable batteries, every bit of battery power is going to be crucial to extending the life of the battery. Sleep modes allow you to power down modules of a microcontroller when not needed so they do not consume valuable power.
So, you saw the many different applications that a microcontroller is used for. But, how do you select the best microcontroller for the job?
There isn’t one specific type of microcontroller that is going to suit all types of application. Every microcontroller will have its own set of pros and cons depending on the application.
We just saw that microcontrollers come in a variety of features. Some might have more memory than others, some might have faster clock speeds, more ADCs, etc.
Depending on the needs of the application, a certain microcontroller with a certain set of features might be a better option than another which has a different set.
For example, if your system needs to do a lot of processing, it will need a bigger CPU and faster clock speeds.
Or, you might be interfacing a lot of sensors, so your microcontroller will need to have multiple ADC channels.
It all comes down to the design criteria of the application and what features the microcontroller offers to meet those criteria.
This article covers microcontroller applications. However, a Microprocessor is another device similar to the microcontroller that could be used for many of these applications.
But, what is the difference between a microcontroller and microprocessor?
The main difference is that a microcontroller is a device that contains the CPU, Memory, Peripherals, all on one chip.
Whereas, a microprocessor chip only contains the CPU. The memory, and peripherals come on separate chips that have to be interfaced with the microprocessor.
Each has their own advantages and disadvantages which will make them appropriate for a certain application.
Microcontrollers cost less, and consume less power, while Microprocessors have faster processing speeds.
Again, this question comes down to the needs of the application.
Microcontrollers are used for applications where complex and complicated tasks need to be done.
However, an application or project might require a task as simple as blinking an LED. In this instance using a microcontroller would be overkill.
You could just use a 555 Timer IC to blink an LED.
It would be analogous to using a saw to cut a piece of paper (where scissors would do the job just fine).
So, before using a microcontroller for a project, see whether its features and abilities are really needed and whether there is another easier way of achieving that particular task.